Data Governance
Within Data Pipes, safeguarding sensitive information is critical, particularly when it comes to structured data sets. This guide aims to provide you with best practices and step-by-step instructions on handling, securing, and maintaining the integrity of sensitive data within tables, be it rows or columns.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a stronger understanding of how to efficiently manage sensitive information in table-based data structures, minimizing risks and ensuring maximum data protection.
Data Security & Classification
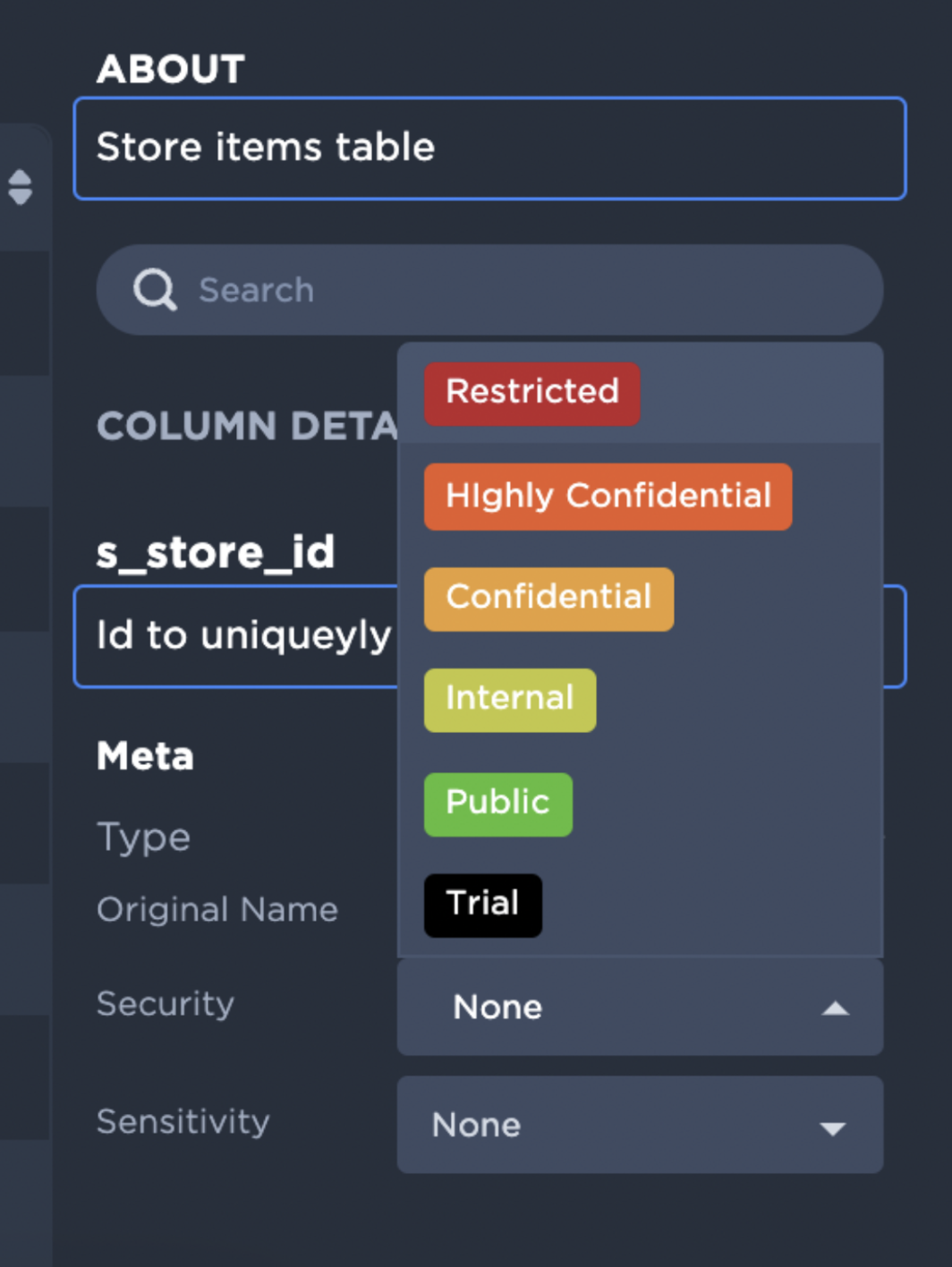
Data Pipes allows defining a security classification for tables and columns. The classification can be used for access control management.
Domain owners can assign data security classifications at the column level. The classification will be applied to that column with immediate effect. Unless a user has explicit access to that column they will not be able to see it. This means that unless they have been explicitly authorized, no user can see any classified information.
Role Based Access Control
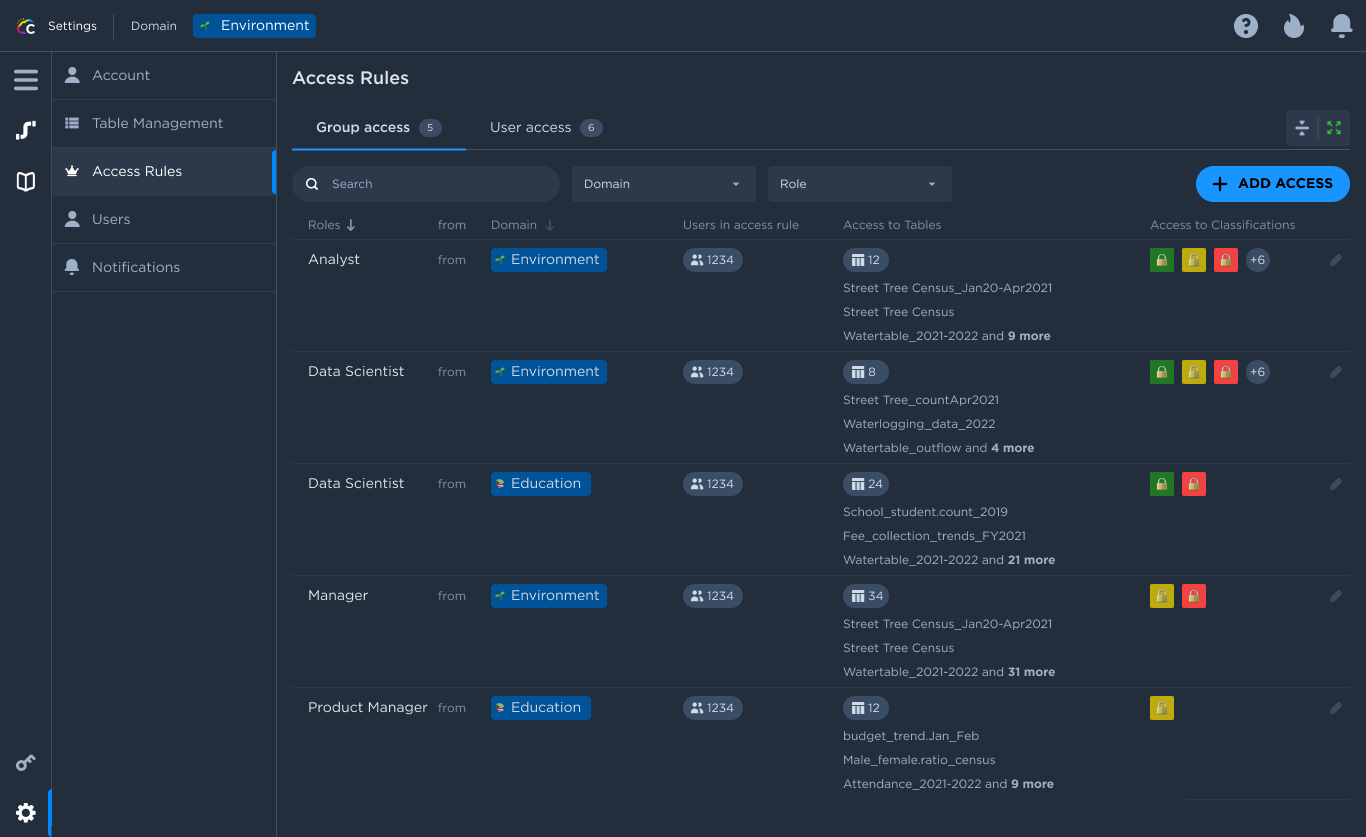
Data Pipes provides a flexible and powerful Role Based Access Control (RBAC) for Data Access control.
Domain Owners are appointed by the Administrator and they will oversee the data access control over all the tables assigned to their domains. Each user is defined by a role and a department, access rules are then created by the domain owners, who can target a user group using a combination of role and department.
It is also possible to create a rule targeting a specific users rather than groups
Column Level Access Control
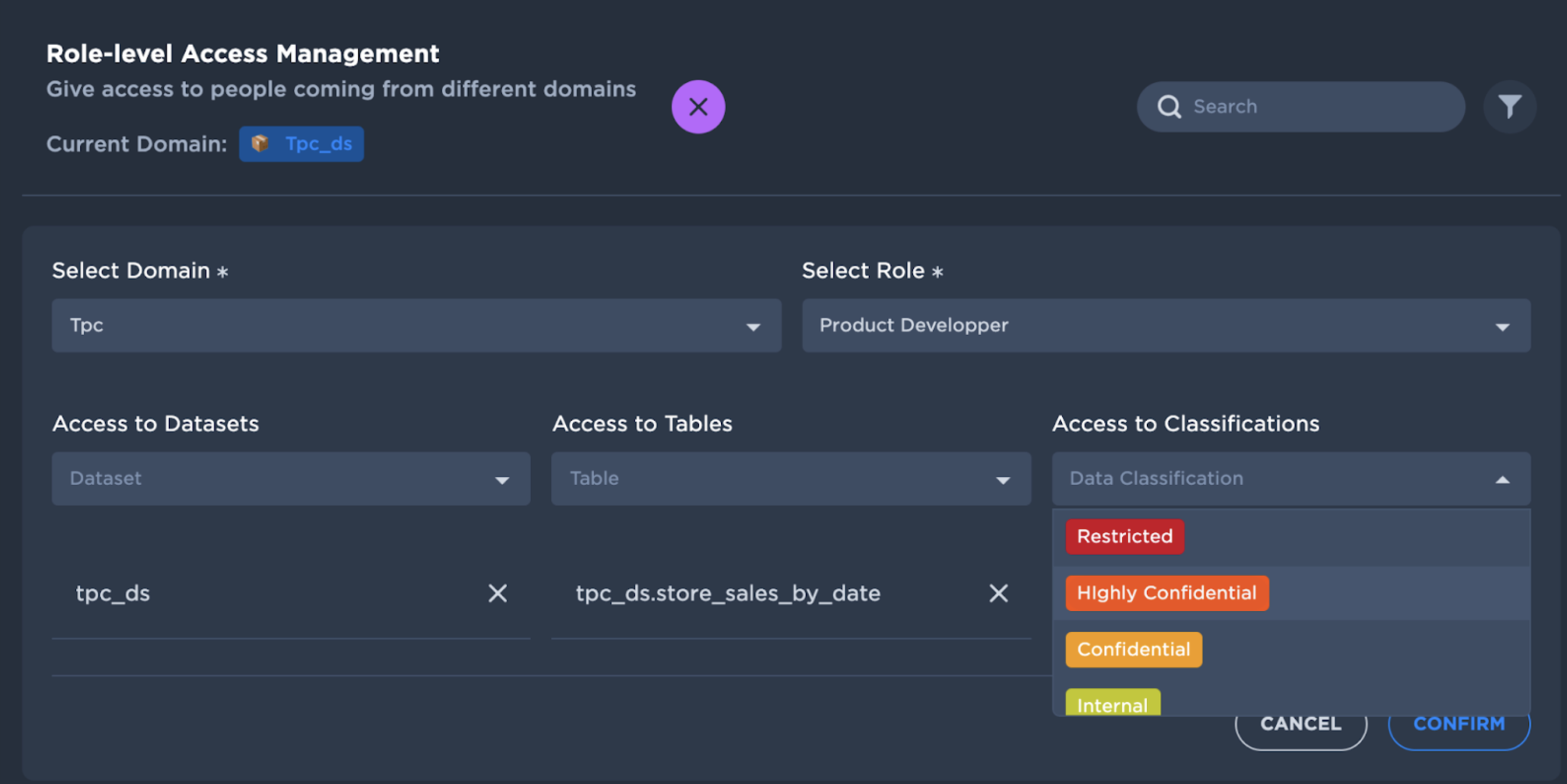
Data Pipes can impose column-level access using the Data Security Classification described above. Domain Owners can tag a column with Data Security Classifications (e.g tagging a column containing user identity number as “Confidential”).
By default, any column tagged with a Data Security Classification will not be accessible to users. Domain Owners can then grant access to Data Security Classification in any Data Access Rule.
Auditing and Reporting
Data Pipes logs a wide variety of information for audit and reporting purposes. Data Office Administrators can download these logs as a CSV.
Data Pipes logs all administrative actions performed by the Data Office Administrators, including creating or editing domain and roles, granting or revoking domains and user management actions.
Data Pipes continuously logs changes to data access rules, so that we have access to historical information on access rules. This log helps keep track of changes in access rules, for example to identify when an access rule was corrected. Information logged includes timestamp, username creating/changing the rule, logic of the rule (tables, targeted users, columns, rows), creation/changes of column level policy tags.
All user resource access are logged: All access to AWS resources (e.g Athena, Glue, etc.) are logged, including username, timestamp, action performed.
All queries executed on the Data Lake are logged with details including username, timestamp, columns queried, query logic. This log allows the identification of unexpected or unauthorised data access. Combined with the “Creation and changes of data access rule” log, Data Office Admins will be able to validate if an incorrect data access rule was abused
